# A tibble: 1 × 8
m2 df pval rmsea ci_lower ci_upper `90% CI` srmsr
<dbl> <int> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <chr> <dbl>
1 513. 325 1.26e-10 0.0141 0.0117 0.0163 [0.0117, 0.0163] 0.0319Evaluating diagnostic classification models
With Stan and measr
Model evaluation
-
Absolute fit: How well does the model represent the observed data?
- Model-level
- Item-level
Relative fit: How do multiple models compare to each other?
Reliability: How consistent and accurate are the classifications?
Absolute model fit
Model-level absolute fit
- Limited information indices based on parameter point estimates
- M2 statistic (Liu et al., 2016)
- Posterior predictive model checks (PPMCs)
Calculating limited information indices
fit_* functions are used for calculating absolute fit indices.
Exercise 1
Open
evaluation.Rmdand run thesetupchunk.Calculate the M2 statistic for the Taylor LCDM model using
add_fit().Extract the M2 statistic. Does the model fit the data?
03:00
# A tibble: 1 × 3
m2 df pval
<dbl> <int> <dbl>
1 183. 162 0.120- The null hypothesis is that our model fits the data
- p-values > .05 indicate acceptable model fit
PPMC: Raw score distribution
- For each iteration, calculate the total number of respondents at each score point
- Calculate the expected number of respondents at each score point
- Calculate the observed number of respondents at each score point
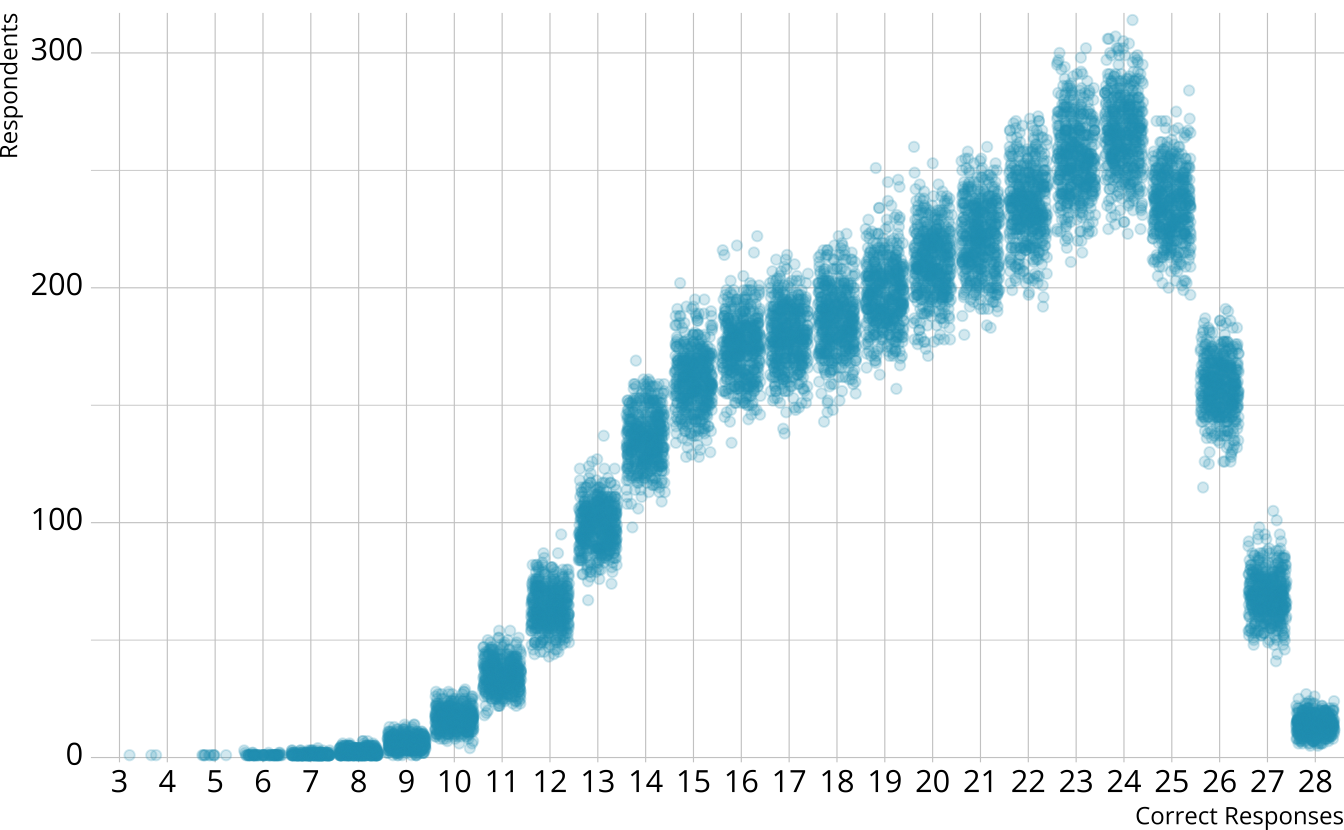
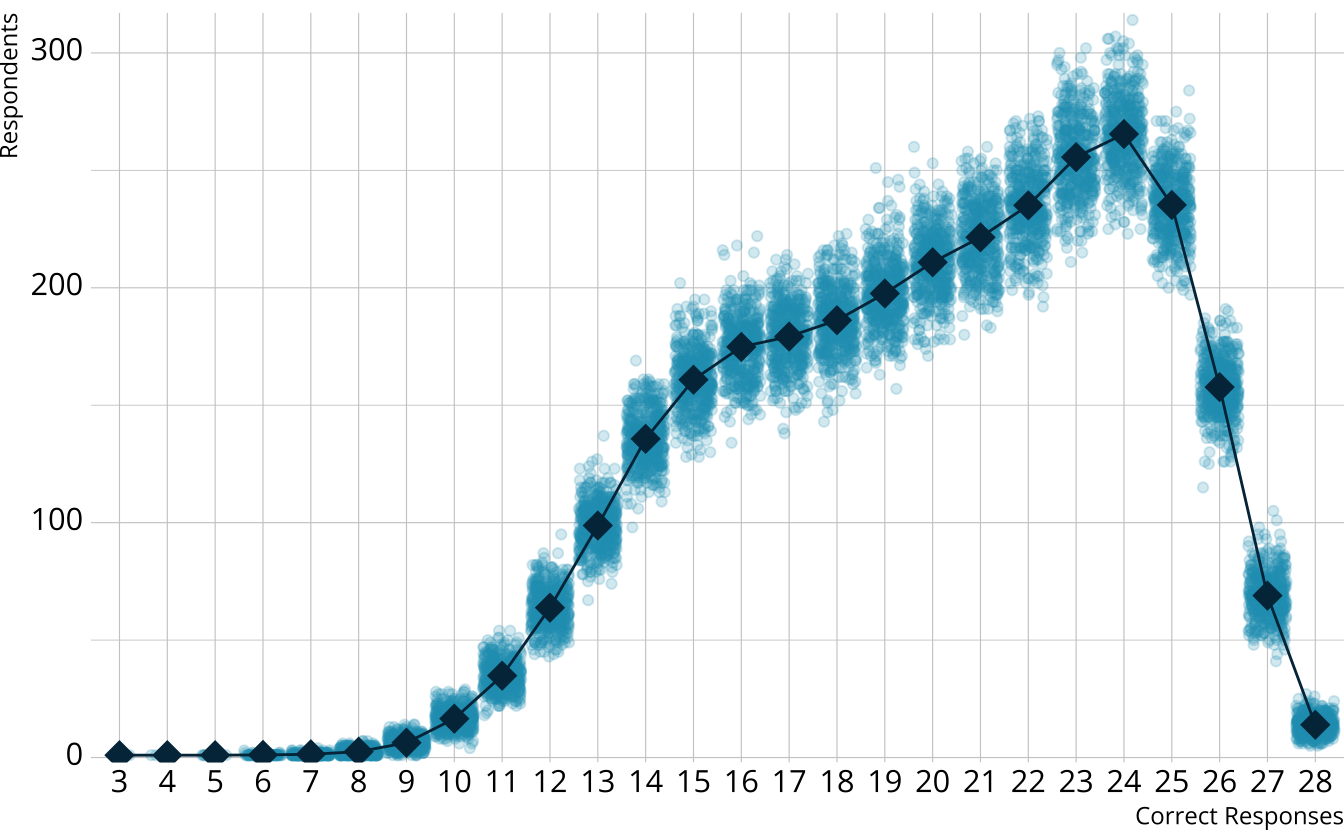
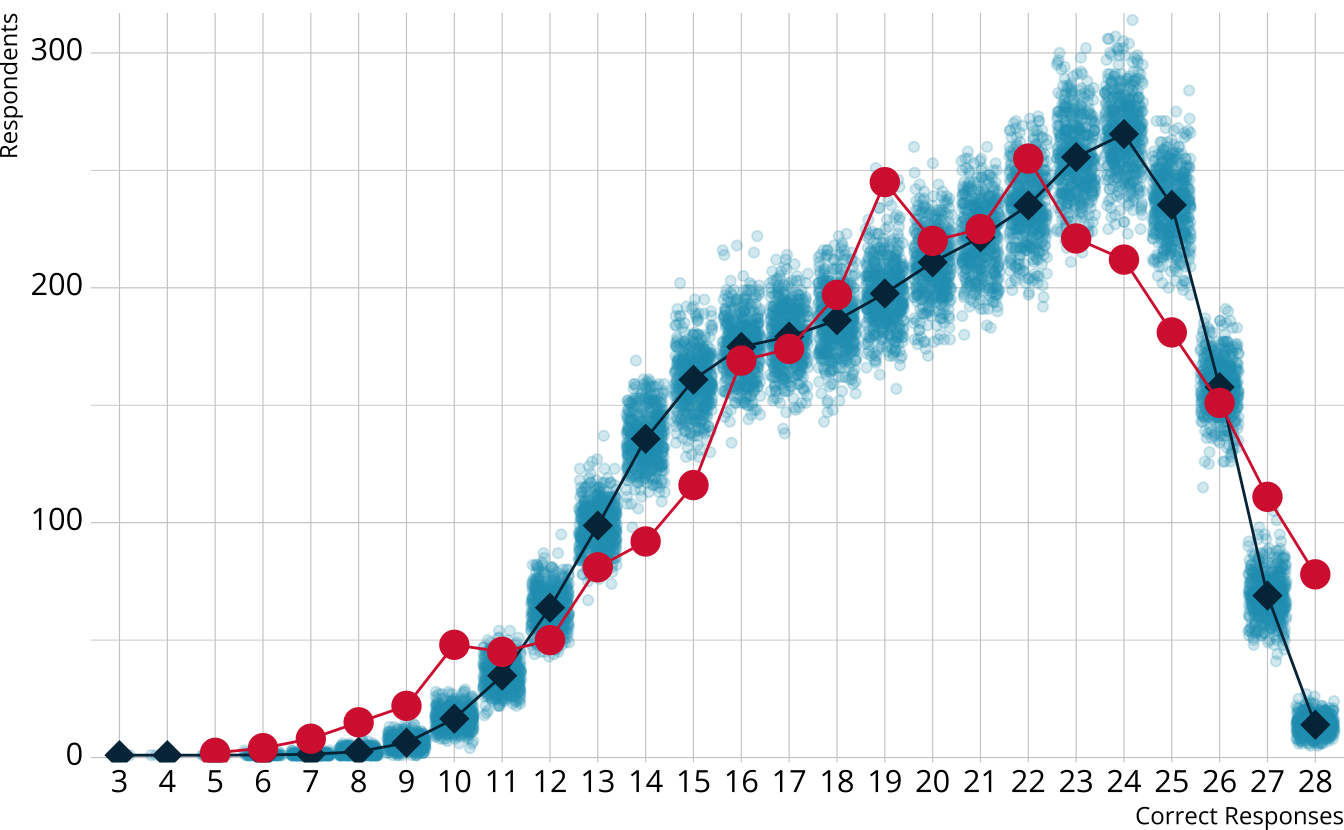
PPMC: \(\chi^2\)
- Calculate a \(\chi^2\)-like statistic comparing the number of respondents at each score point in each iteration to the expectation
- Calculate the \(\chi^2\) value comparing the observed data to the expectation
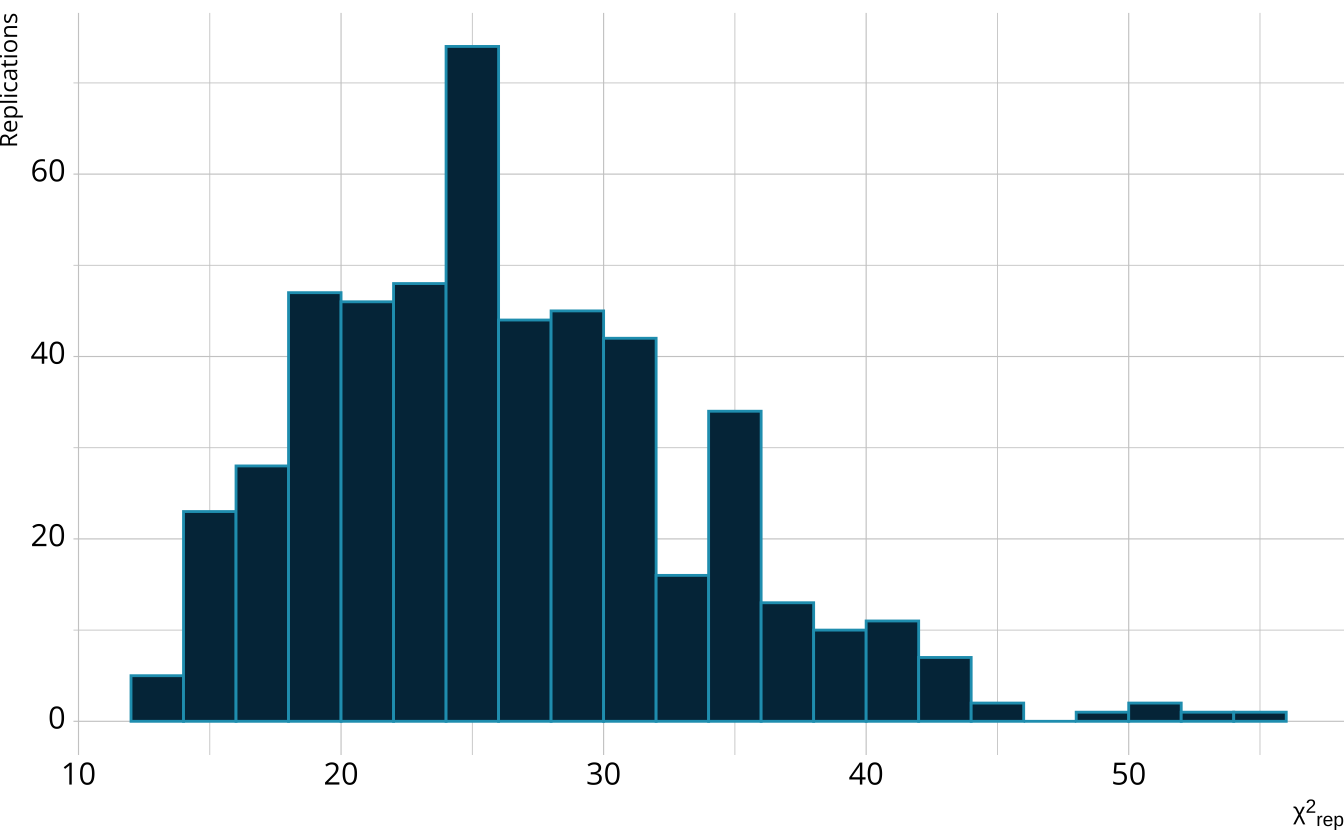
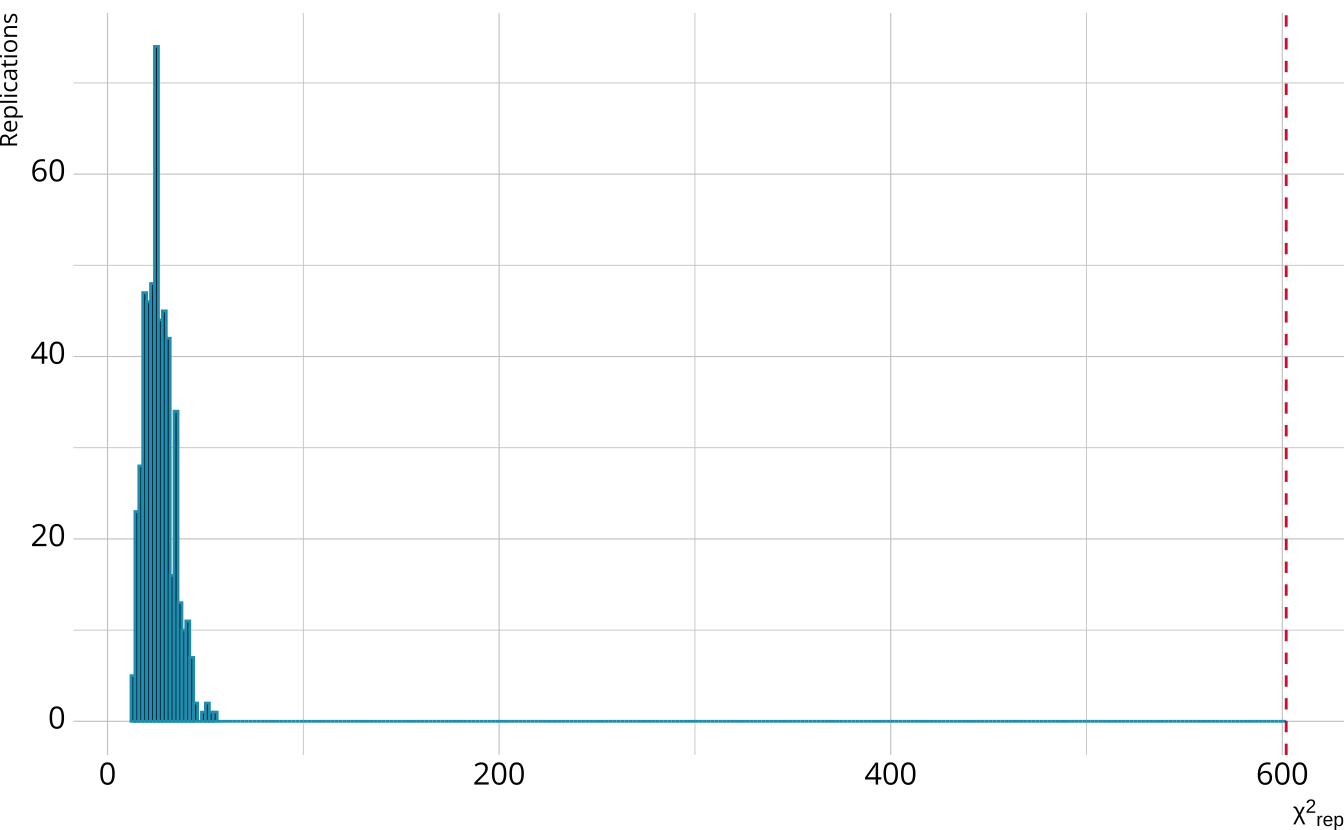
PPMC: ppp
- Calculate the proportion of iterations where the \(\chi^2\)-like statistic from replicated data set exceeds the observed data statistic
- Posterior predictive p-value (ppp)
- Very high values (e.g., >.975) or very low values (e.g., <.025) indicate our observed value is far in the tails of what the model would predict
- Poor model fit
- Ideally, we’d like ppp values close to .5
PPMCs with measr
Exercise 2
Calculate the raw score PPMC for the Taylor LCDM
Does the model fit the observed data?
04:00
taylor_lcdm <- add_fit(taylor_lcdm, method = "ppmc", item_fit = NULL)
measr_extract(taylor_lcdm, "ppmc_raw_score")# A tibble: 1 × 5
obs_chisq ppmc_mean `2.5%` `97.5%` ppp
<dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
1 18.5 23.7 11.8 44.0 0.719- The ppp value is between .025 and .975
- Model fit appears to be adequate.
Item-level fit
Diagnose problems with model-level
Identify particular items that may not be performing as expected
Identify potential dimensionality issues
Item-level fit with measr
- Currently support two-measures of item-level fit using PPMCs:
- Conditional probability of each class providing a correct response (\(\pi\) matrix)
- Item pair odds ratios
Calculating item-level fit
$item_fit
$item_fit$odds_ratio
# A tibble: 378 × 7
item_1 item_2 obs_or ppmc_mean `2.5%` `97.5%` ppp
<fct> <fct> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
1 E1 E2 1.61 1.39 1.08 1.82 0.105
2 E1 E3 1.42 1.49 1.22 1.79 0.642
3 E1 E4 1.58 1.39 1.12 1.71 0.108
4 E1 E5 1.68 1.47 1.10 1.92 0.162
5 E1 E6 1.64 1.38 1.07 1.79 0.089
6 E1 E7 1.99 1.71 1.39 2.11 0.0745
7 E1 E8 1.54 1.58 1.14 2.07 0.534
8 E1 E9 1.18 1.27 1.02 1.54 0.731
9 E1 E10 1.82 1.59 1.28 1.93 0.104
10 E1 E11 1.61 1.63 1.30 2.00 0.536
# ℹ 368 more rowsExtracting item-level fit
# A tibble: 224 × 7
item class obs_cond_pval ppmc_mean `2.5%` `97.5%` ppp
<fct> <chr> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
1 E1 [0,0,0] 0.701 0.694 0.661 0.723 0.322
2 E1 [1,0,0] 0.790 0.801 0.712 0.909 0.535
3 E1 [0,1,0] 0.992 0.810 0.758 0.865 0
4 E1 [0,0,1] 0.608 0.694 0.661 0.723 1
5 E1 [1,1,0] 0.995 0.930 0.908 0.952 0
6 E1 [1,0,1] 0.481 0.801 0.712 0.909 1
7 E1 [0,1,1] 0.832 0.810 0.758 0.865 0.200
8 E1 [1,1,1] 0.926 0.930 0.908 0.952 0.646
9 E2 [0,0,0] 0.741 0.739 0.708 0.766 0.463
10 E2 [1,0,0] 0.832 0.739 0.708 0.766 0
# ℹ 214 more rows# A tibble: 378 × 7
item_1 item_2 obs_or ppmc_mean `2.5%` `97.5%` ppp
<fct> <fct> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
1 E1 E2 1.61 1.39 1.08 1.82 0.105
2 E1 E3 1.42 1.49 1.22 1.79 0.642
3 E1 E4 1.58 1.39 1.12 1.71 0.108
4 E1 E5 1.68 1.47 1.10 1.92 0.162
5 E1 E6 1.64 1.38 1.07 1.79 0.089
6 E1 E7 1.99 1.71 1.39 2.11 0.0745
7 E1 E8 1.54 1.58 1.14 2.07 0.534
8 E1 E9 1.18 1.27 1.02 1.54 0.731
9 E1 E10 1.82 1.59 1.28 1.93 0.104
10 E1 E11 1.61 1.63 1.30 2.00 0.536
# ℹ 368 more rowsFlagging item-level fit
# A tibble: 106 × 7
item class obs_cond_pval ppmc_mean `2.5%` `97.5%` ppp
<fct> <chr> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
1 E1 [0,1,0] 0.992 0.810 0.758 0.865 0
2 E1 [0,0,1] 0.608 0.694 0.661 0.723 1
3 E1 [1,1,0] 0.995 0.930 0.908 0.952 0
4 E1 [1,0,1] 0.481 0.801 0.712 0.909 1
5 E2 [1,0,0] 0.832 0.739 0.708 0.766 0
6 E2 [0,1,0] 1 0.906 0.886 0.926 0
7 E2 [0,0,1] 0.696 0.739 0.708 0.766 0.993
8 E2 [1,1,0] 0.972 0.906 0.886 0.926 0
9 E2 [1,0,1] 0.425 0.739 0.708 0.766 1
10 E3 [0,1,0] 0.355 0.414 0.381 0.448 1
# ℹ 96 more rows# A tibble: 80 × 7
item_1 item_2 obs_or ppmc_mean `2.5%` `97.5%` ppp
<fct> <fct> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
1 E1 E13 1.80 1.44 1.13 1.78 0.0175
2 E1 E17 2.02 1.40 1.03 1.82 0.006
3 E1 E26 1.61 1.24 1.00 1.50 0.004
4 E1 E28 1.86 1.40 1.07 1.74 0.0045
5 E2 E4 1.73 1.37 1.10 1.69 0.0145
6 E2 E14 1.64 1.23 0.994 1.52 0.003
7 E2 E15 1.92 1.46 1.08 1.90 0.02
8 E4 E5 2.81 2.09 1.58 2.75 0.0135
9 E4 E8 2.14 1.55 1.17 2.02 0.009
10 E4 E13 1.80 1.27 1.07 1.52 0
# ℹ 70 more rowsPatterns of item-level misfit
Exercise 3
Calculate PPMCs for the conditional probabilities and odds ratios for the Taylor model
What do the results tell us about the model?
05:00
# A tibble: 21 × 7
item class obs_cond_pval ppmc_mean `2.5%` `97.5%` ppp
<fct> <chr> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
1 1 [1,1,0] 0.972 0.880 0.831 0.923 0
2 3 [0,0,1] 0.519 0.444 0.377 0.511 0.011
3 5 [0,1,0] 0.417 0.333 0.262 0.407 0.015
4 5 [0,0,1] 0.303 0.405 0.335 0.477 0.998
5 6 [0,0,1] 0.198 0.269 0.206 0.337 0.986
6 6 [1,0,1] 0.173 0.269 0.206 0.337 0.998
7 7 [1,0,0] 0.0750 0.150 0.0826 0.220 0.987
8 7 [0,1,0] 0.964 0.882 0.810 0.949 0.006
9 9 [0,0,1] 0.794 0.724 0.662 0.788 0.018
10 13 [0,1,0] 0.325 0.452 0.383 0.520 1
# ℹ 11 more rowsRelative model fit
Model comparisons
- Doesn’t give us information whether or not a model fits the data, only compares competing models to each other
- Should be evaluated in conjunction with absolute model fit
- Implemented with the loo package
- PSIS-LOO (Vehtari, 2017)
- WAIC (Watanabe, 2010)
Relative fit with measr
Computed from 2000 by 2922 log-likelihood matrix.
Estimate SE
elpd_loo -42817.3 226.1
p_loo 77.1 0.8
looic 85634.5 452.1
------
MCSE of elpd_loo is 0.2.
MCSE and ESS estimates assume independent draws (r_eff=1).
All Pareto k estimates are good (k < 0.7).
See help('pareto-k-diagnostic') for details.Comparing models
First, we need another model to compare
ecpe_dina <- measr_dcm(
data = ecpe_data, qmatrix = ecpe_qmatrix,
resp_id = "resp_id", item_id = "item_id",
type = "dina",
method = "mcmc", backend = "cmdstanr",
iter_warmup = 1000, iter_sampling = 500,
chains = 4, parallel_chains = 4,
file = "fits/ecpe-dina"
)
ecpe_dina <- add_criterion(ecpe_dina, criterion = "loo")loo_compare()
elpd_diff se_diff
lcdm 0.0 0.0
dina -674.2 29.7 - LCDM is the preferred model
- Preferred does not imply “good”
- Remember, the LCDM showed poor absolute fit
- Difference is much larger than the standard error of the difference
- Approximate threshold: Absolute difference is greater than 2.5 × standard error of the difference (Bengio & Grandvalet, 2004)
Exercise 4
Estimate a DINA model for the Taylor data
Add PSIS-LOO and WAIC criteria to both the LCDM and DINA models for the Taylor data
-
Use
loo_compare()to compare the LCDM and DINA models- What do the findings tell us?
- Can you explain the results?
15:00
Reliability
Reliability methods
Reporting reliability depends on how results are estimated and reported
-
Reliability for:
- Profile-level classification
- Attribute-level classification
- Attribute-level probability of proficiency
Reliability with measr
$pattern_reliability
p_a p_c
0.7389797 0.6639670
$map_reliability
$map_reliability$accuracy
# A tibble: 3 × 8
attribute acc lambda_a kappa_a youden_a tetra_a tp_a tn_a
<chr> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
1 morphosyntactic 0.896 0.729 0.786 0.775 0.942 0.851 0.924
2 cohesive 0.852 0.675 0.703 0.699 0.892 0.877 0.822
3 lexical 0.916 0.750 0.611 0.802 0.959 0.947 0.854
$map_reliability$consistency
# A tibble: 3 × 10
attribute consist lambda_c kappa_c youden_c tetra_c tp_c tn_c gammak
<chr> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
1 morphosyntactic 0.834 0.557 0.685 0.646 0.853 0.779 0.867 0.852
2 cohesive 0.807 0.563 0.681 0.608 0.818 0.827 0.782 0.789
3 lexical 0.856 0.553 0.625 0.670 0.876 0.894 0.776 0.880
# ℹ 1 more variable: pc_prime <dbl>
$eap_reliability
# A tibble: 3 × 5
attribute rho_pf rho_bs rho_i rho_tb
<chr> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
1 morphosyntactic 0.735 0.687 0.573 0.884
2 cohesive 0.729 0.574 0.506 0.785
3 lexical 0.759 0.730 0.587 0.915Profile-level classification
# A tibble: 2,922 × 9
resp_id `[0,0,0]` `[1,0,0]` `[0,1,0]` `[0,0,1]` `[1,1,0]` `[1,0,1]` `[0,1,1]`
<fct> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
1 1 7.78e-6 9.85e-5 5.14e-7 0.00131 0.0000877 0.0438 0.00207
2 2 5.88e-6 7.44e-5 1.97e-7 0.00303 0.0000339 0.0977 0.00195
3 3 5.64e-6 1.73e-5 1.71e-6 0.00206 0.0000687 0.00974 0.0150
4 4 3.24e-7 4.06e-6 9.83e-8 0.000295 0.0000168 0.00988 0.00215
5 5 1.18e-3 8.27e-3 3.55e-4 0.00127 0.0354 0.00935 0.00919
6 6 3.01e-6 1.53e-5 9.13e-7 0.000913 0.0000633 0.00983 0.00662
7 7 3.01e-6 1.53e-5 9.13e-7 0.000913 0.0000633 0.00983 0.00662
8 8 3.79e-2 8.83e-5 1.35e-3 0.518 0.0000275 0.000594 0.438
9 9 6.60e-5 1.99e-4 1.98e-5 0.00660 0.000936 0.00936 0.0480
10 10 4.14e-1 4.03e-1 3.65e-3 0.0387 0.0621 0.0181 0.00797
# ℹ 2,912 more rows
# ℹ 1 more variable: `[1,1,1]` <dbl># A tibble: 2,922 × 3
resp_id profile prob
<fct> <chr> <dbl>
1 1 [1,1,1] 0.953
2 2 [1,1,1] 0.897
3 3 [1,1,1] 0.973
4 4 [1,1,1] 0.988
5 5 [1,1,1] 0.935
6 6 [1,1,1] 0.983
7 7 [1,1,1] 0.983
8 8 [0,0,1] 0.518
9 9 [1,1,1] 0.935
10 10 [0,0,0] 0.414
# ℹ 2,912 more rows# A tibble: 1 × 2
accuracy consistency
<dbl> <dbl>
1 0.739 0.664- Estimating classification consistency and accuracy for cognitive diagnostic assessment (Cui et al., 2012)
Attribute-level classification
# A tibble: 2,922 × 4
resp_id morphosyntactic cohesive lexical
<fct> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
1 1 0.997 0.955 1.00
2 2 0.995 0.899 1.00
3 3 0.983 0.988 1.00
4 4 0.998 0.990 1.00
5 5 0.988 0.980 0.955
6 6 0.992 0.989 1.00
7 7 0.992 0.989 1.00
8 8 0.00451 0.443 0.961
9 9 0.945 0.984 0.999
10 10 0.535 0.126 0.117
# ℹ 2,912 more rows# A tibble: 2,922 × 4
resp_id morphosyntactic cohesive lexical
<fct> <int> <int> <int>
1 1 1 1 1
2 2 1 1 1
3 3 1 1 1
4 4 1 1 1
5 5 1 1 1
6 6 1 1 1
7 7 1 1 1
8 8 0 0 1
9 9 1 1 1
10 10 1 0 0
# ℹ 2,912 more rows# A tibble: 3 × 3
attribute accuracy consistency
<chr> <dbl> <dbl>
1 morphosyntactic 0.896 0.834
2 cohesive 0.852 0.807
3 lexical 0.916 0.856- Measures of agreement to assess attribute-level classification accuracy and consistency for cognitive diagnostic assessments (Johnson & Sinharay, 2018)
Attribute-level probabilities
# A tibble: 2,922 × 4
resp_id morphosyntactic cohesive lexical
<fct> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
1 1 0.997 0.955 1.00
2 2 0.995 0.899 1.00
3 3 0.983 0.988 1.00
4 4 0.998 0.990 1.00
5 5 0.988 0.980 0.955
6 6 0.992 0.989 1.00
7 7 0.992 0.989 1.00
8 8 0.00451 0.443 0.961
9 9 0.945 0.984 0.999
10 10 0.535 0.126 0.117
# ℹ 2,912 more rows# A tibble: 3 × 2
attribute informational
<chr> <dbl>
1 morphosyntactic 0.573
2 cohesive 0.506
3 lexical 0.587- The reliability of the posterior probability of skill attainment in diagnostic classification models (Johnson & Sinharay, 2020)
Exercise 5
Add reliability information to the Taylor LCDM and DINA models
Examine the attribute classification indices for both models
04:00
# A tibble: 3 × 3
attribute accuracy consistency
<chr> <dbl> <dbl>
1 songwriting 0.969 0.941
2 production 0.910 0.837
3 vocals 0.913 0.843Evaluating diagnostic classification models
With Stan and measr